Beginner's Guide for Stroke Treatment
By Canada Cloud Pharmacy | Published Wednesday 30 June 2021
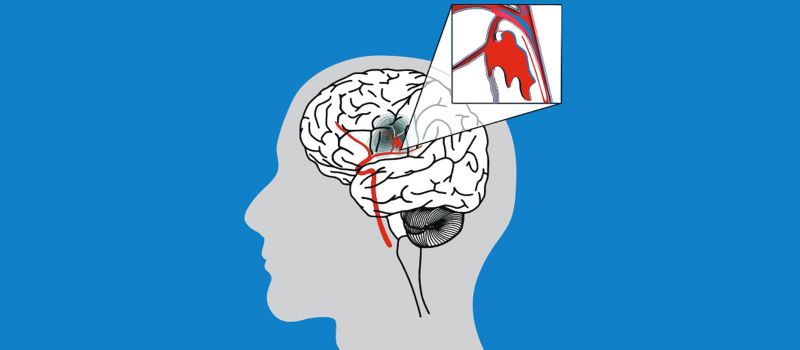
Treating a stroke is a complicated process and can involve correcting the underlying pathology, administering medications to prevent future adverse events, and rehabilitative exercises to help the patient recover from the side effects of stroke.
The treatments for an ischemic or a hemorrhagic stroke differ as their causes and effects on the brain differ. The decision to use a treatment option depends on the type of stroke the patient is having. The doctor will do many blood tests and radiological exams to determine the type of stroke and after making a diagnosis, he/she will decide about the required treatments.
Following are treatment options used to treat ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke.
Ischemic stroke: In this type of stroke, the initial aim of treatment is the restoration of blood flow to the brain.
-
Thrombolytic drugs: The gold standard treatment for breaking up the clot is recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) also called alteplase. This dissolves the clot and restores blood flow to the brain. It is best to administer this drug within 4.5 hours after the initial symptoms of a stroke.
-
Endovascular procedures: In these procedures, the doctors directly remove the clot from the blood vessel or administer a thrombolytic agent directly at the point of clotting by inserting a thin tube into the blood vessel.
-
To decrease the risk of another stroke, the doctor may prescribe aspirin, blood pressure medications, statins, anticoagulants and may recommend procedures like carotid endarterectomy and angioplasty with stent placement.
Hemorrhagic stroke: In this type of stroke, the treatment aims to control the bleeding on the brain and reduce excess pressure on the brain tissue due to excessive fluid.
-
Initial treatment: Initially, the doctor may administer blood products to counteract the effects of any blood-thinning drugs the patients may be taking. The doctor may also give drugs to reduce intracranial pressure, reduce blood pressure, and prevent seizures.
-
Surgery: In some cases, the surgery may be indicated. The surgeon will remove the excess blood through open surgery. The surgery may also be performed to repair blood vessels, correct vessel abnormalities, and place clamps on aneurysm to decrease blood flow.
-
Coiling: In this procedure, a detachable coil is inserted into the aneurysm through an intravascular catheter. This results in blockage of blood flow to the aneurysm and allows the blood to clot.
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery: It is a minimally invasive procedure that is used to correct blood vessel malformations.



 Canadian Company
Canadian Company 



 Sign In
Sign In
 Home
Home 
 About Us
About Us 
 How to order
How to order 
 Products
Products 



